|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
VIDEO. Learn about cannabinoids, THC, CBD, CBN, Topical vs Transdermal. Meet Allie Greenstone as she trains the Phog Center crew.
Need help finding the right medicine for you? Stop by The Phog Center, 2270 Palmetto Ave, Pacifica and sit down with one of our Budtenders for a one-on-one consultation. Order online at www.phogcenter.com for pick-up or delivery or give us a call, 844-504-8771, we’ll bring the relief to the comfort of your home 😊🏡 ~ The Phog Center’s Jesus Sahagun
A cannabinoid is one of a class of diverse chemical compounds that acts on cannabinoid receptors in cells that alter neurotransmitter release in the brain. Ligands for these receptor proteins include the endocannabinoids (produced naturally in the body by animals), the phytocannabinoids (found in cannabis and some other plants), and synthetic cannabinoids(manufactured artificially). The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is another major constituent of the plant. There are at least 113 different cannabinoids isolated from cannabis, exhibiting varied effects. ~ Wikipedia
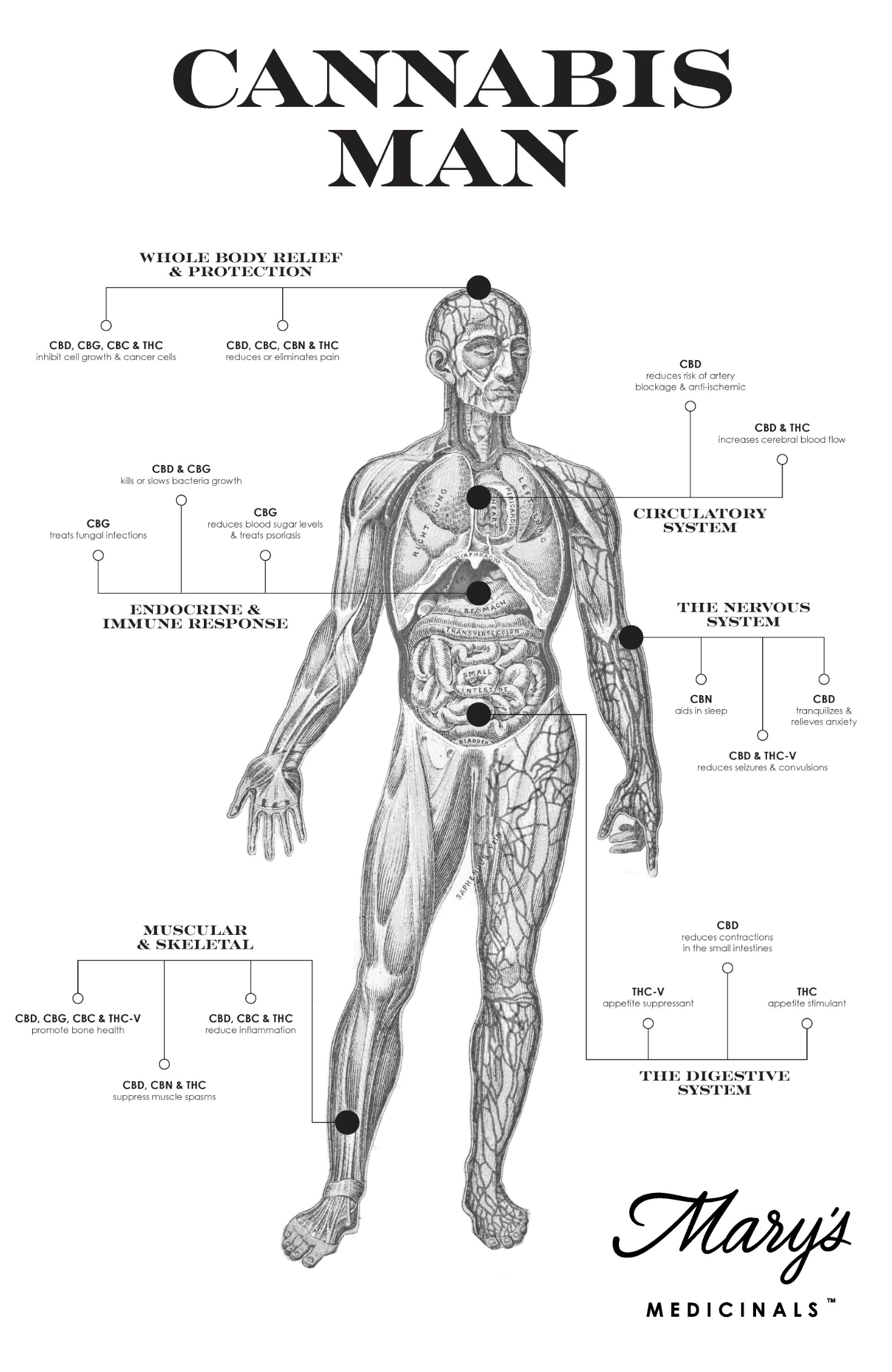
SCIENCE OF CANNABINOIDS
~ Credit: Mary’s Medicinals (also Mary’s Nutritionals and Mary’s Whole Pet)
Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds within cannabis that are reported to relieve many ailments. Cannabinoids resemble endocannabinoids, compounds our bodies naturally produce to balance and control communication between cells. Researchers believe that unpleasant symptoms and diseases occur when a deficiency or problem affects the endocannabinoid system.
When cannabis is administered, cannabinoids bind to receptor sites in the brain and body. Cannabinoids have different effects based on which receptors they bind to. For example, CBN (Cannabinol) binds with CB-2 receptors located throughout the body, which may explain why patients report that it is a powerful analgesic. With an increasing understanding of the effects of cannabinoids, patients can now tailor their cannabinoid consumption to the type of relief they need.
Terpenes and terpenoids are the primary constituents of the essential oils of many types of plants and flowers. They give cannabis varieties their distinctive properties, aromas, and flavors. During the process of extracting essential oils from cannabis, terpenes are often lost. However, Mary’s strives to maintain or replenish vital terpenes in the creation of all of its products.
UNDERSTANDING BIOAVAILABILITY AND DOSING
Research shows that transdermal delivery is the most effective method of delivering cannabis to the body as it enters the blood stream directly. When smoked or eaten, patients may lose up to 70 percent of the cannabis consumed via air vaporization, metabolism and stomach acid, which is inefficient and makes accurate dosing difficult. Mary’s transdermal products are so effective that the dosing of a standard 10mg patch may be equivalent to that of an 80mg edible.
With optimized bioavailability, Mary’s products offer a reliable, consistent dosage. Like all medicines, an individual’s dosage is based on many factors such as age, body composition, diagnosis, etc. One patch is a typical dose for most patients, although some prefer to cut a patch into halves or even quarters, while others may use more than one patch to attain relief.